

Plateau pressure (Pplat) (pressure used to keep air in the lungs) is determined by an inspiratory hold maneuver in which the patient is given a fixed volume of air. Things that may increase Peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) could be increased secretions, bronchospasm, biting down on ventilation tubing, and decreased lung compliance. Peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) increases with any airway resistance. The risk for barotrauma increases whenever the peak pressures and plateau pressures become elevated to the same degree 2. Peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) should be kept below 20 to 25 cm H2O whenever positive-pressure ventilation is required, especially if pneumothoraces, or fresh bronchial or pulmonary suture lines, are present. Normal peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) is 25-30 cm H2O. In mechanical ventilation the number reflects a positive pressure in centimeters of water pressure (cm H2O). Consequently, Pplat can never be more than peak inspiratory pressure (PIP), because there’s always going to be intrinsic resistance which must be overcome by P resistance. In other words: Peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) = Pplat + P resistance. The peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) is the sum of the plateau pressure (Pplat) (pressure used to keep air in the lungs) and pressure used to overcome airway resistance (P resistance) to get the air into the lungs (elastic recoil of the lungs and chest wall, friction, etc.). PEEP anesthesia cardiac surgery coronary artery bypass grafting mechanical ventilation.Peak inspiratory pressure (PIP) is the highest level of pressure applied to the lungs during inhalation 1. Thus, use of 8 cm H2O PEEP in these patients without a clinical indication, although likely not harmful, does not seem beneficial. Patients being mechanically ventilated after cardiac operations with an initial postoperative PEEP setting of 8 versus 5 cm H2O differed significantly only on hospital LOS but the difference was likely clinically unimportant. There was a slight but likely clinically unimportant difference in hospital LOS (7.7 vs 7.4 days, PEEP = 8 vs 5, P <. 057), but were not statistically different. Aspiration pneumonia occurrence approached a significant difference (0.06% vs 0.21%, P value =. The groups did not differ on the occurrence of pneumonia (0.43% vs 0.60%, P =. There was no difference in initial postoperative intubation time between the PEEP of 8 cm H2O and the PEEP of 5 cm H2O patient groups (mean 11.9 vs 12.0 hours, P =. Propensity score matching was used to compare patients with an initial postoperative PEEP setting of 8 cm H2O (n = 4722 ) with those who had PEEP of 5 cm H2O (n = 13 535 ) on the primary and secondary outcomes listed earlier. The electronic medical records of patients who were mechanically ventilated after isolated coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or combined CABG and valve operations were reviewed.
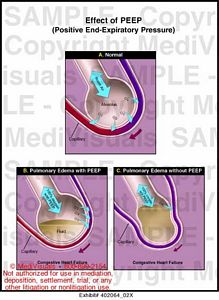
The aim of this investigation was to compare the 2 most common postoperative initial PEEP settings at our institution, 8 and 5 cm H2O, on postoperative initial tracheal intubation time (primary outcome) cardiovascular intensive care unit (CVICU) hospital length of stay (LOS) occurrence of pneumonia and hospital mortality (secondary outcomes). Postoperative positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) selection in patients who are mechanically ventilated after cardiac operations often seems random.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
